Module 4: Digital Content Creation
We are witnessing a period in which digital technologies are getting more and more involved in our lives and their usage areas are expanding, and we even contribute to this process. We can give an example of the use of social media to reflect this situation. While sharing, we use information and data literacy, communication elements, digital content production with selected or created images/videos/text, e-security including copyrights, and all problem solving skills that will solve the problems that occur in the sharing process. We experience this example in the content prepared for a web page, in the learning object prepared for the course, in the prepared report and in many other areas. As can be seen in these multidimensional processes, we frequently use DigComp competence areas in our lives with its integrated structure. In this module, we will try to introduce you to DigComp’s “Digital Content Creation” main competence area.
What is Digital Content Creation in 3 Words?
What do you think about creating digital content in the classroom? Write 1 word in each of the form fields below and describe it with a total of three words.
DigComp framework offers a roadmap that will enable swimming in the digital ocean consisting of 5 dimensions that will support each other by considering the digital skills and competencies required by the current century. The DigComp Framework includes the knowledge and skills needed to use digital technologies in many areas such as searching – finding – selecting information, creating – sharing – managing content, communicating effectively and collaborating, and problem solving. The third main area of the EU Digital Competence Framework (DigComp 2.1) is digital content creation. Observable competencies that reflect effective use in the main area of digital content creation, as well as in the main areas of information and data literacy, communication and cooperation, come to the fore. In this context, it is observed that the digital competence definition of Lankshear and Knobel, which we shared with you in our introductory module, as “the sum of the knowledge, skills and attitudes that an individual employs in terms of accessing, understanding and using information in various formats in different digital environments” draws the framework of creating digital content. Different digital media and different formats highlighted in the definition also reflect the importance of creating digital content.
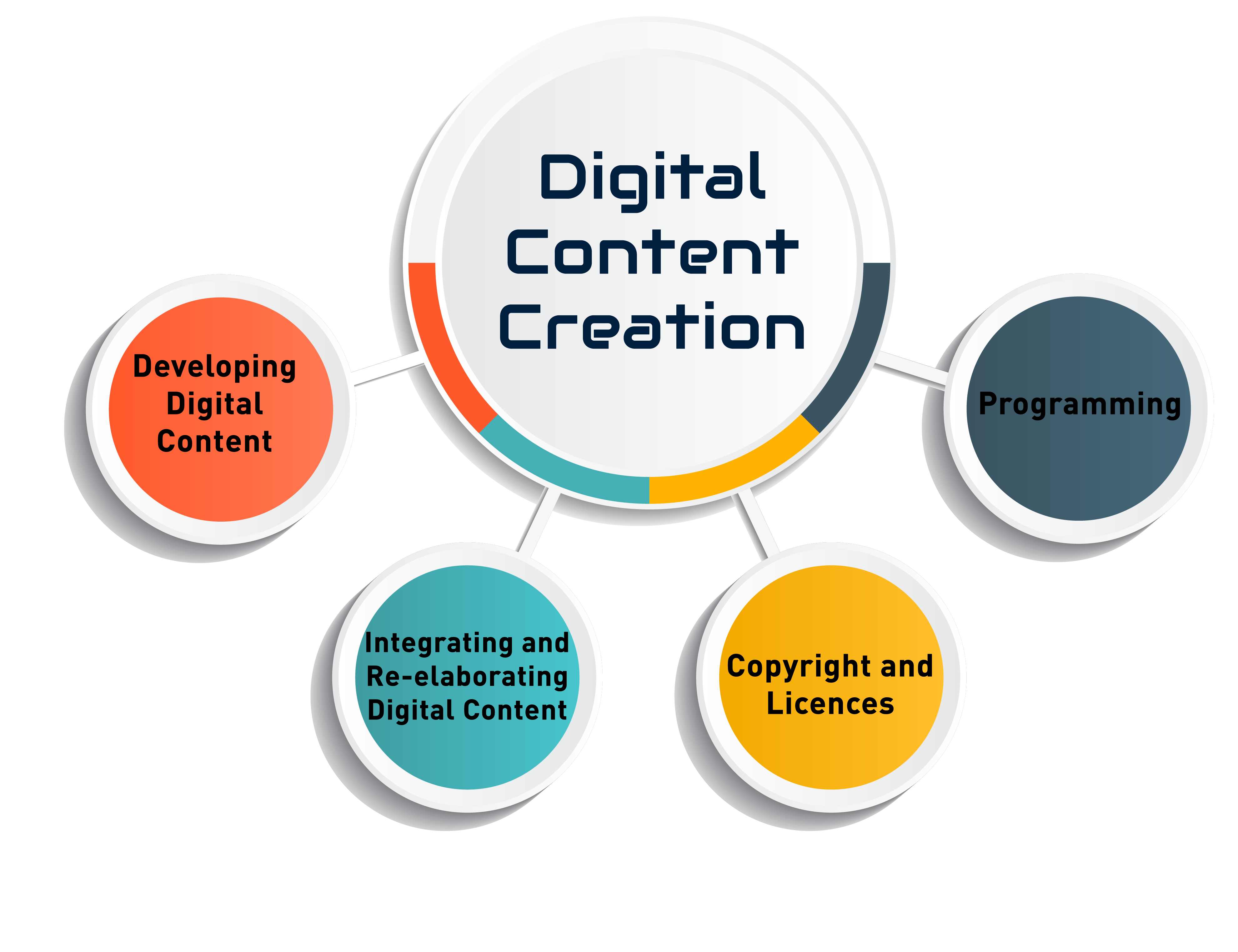
Digital content creation includes text documents, graphics, images, videos, music, sounds, multimedia, web pages stored using standard file formats, with an emphasis on various digital formats, including 3D prints, paid and/or free, open and/or closed license, It covers all proprietary and/or unregistered file types. Digital environments are all connected places and technological tools that enable file sharing and creation by technology and digital devices, where all digital tools (such as mobile phone network) are active, usually including the internet or other network infrastructures. Records and evidence of individuals’ interactions in digital environments constitute the digital footprints of individuals. In DigComp, the concept of digital media is used for all digital actions, including the digital footprint, without emphasis on a particular technology or tool. Digital technology is used to create, display, distribute, modify, store, retrieve, transmit and transfer information digitally (e.g., personal computers, desktops, laptops, netbooks, tablet computers, smartphones, interactive/smartboards, projectors). machines, mobile phones, PDAs, game consoles, media players, e-book readers, digital televisions, robots) are products and devices. In short, all of the digital tools used for a specific purpose or to perform the functions of processing, communication, content creation, security or problem solving for a specific information constitute digital technologies.In the light of this preliminary information, the third main area of our DigComp Framework, “Digital Content Creation” is defined as follows. “Developing knowledge and/or content or integrating existing knowledge with new ones, knowing how copyright and licenses will apply to create and edit digital content. It is also knowing how to give and create clear instructions for a computer system.” As reflected in the definition, this core competency covers the development of digital content, integrating and revising digital content, copyrights and licenses, programming.
3.1. Digital Content Creation
This area of competence includes creating content in different formats including multimedia, editing and developing content created by himself or others, and expressing himself creatively using digital media and technologies. This sub-competence area, individuals should be able to use basic package programs or tools to create simple content in different formats (text, sound, table, pictures, etc.) and produce digital content in different formats (text, tables, pictures, sound, mind maps, diagrams, films, etc.), including multimedia and use various digital tools that will enable them to create original and original multimedia outputs by producing digital content in different formats, on different platforms, in different environments and with different tools.
In summary, digital content development sub-competence includes knowledge,skills and attitude that enable creating digital content in different formats, choosing the most suitable digital technologies and tools for this content, expressing oneself using multimedia in various digital environments, being both a producer and a consumer by paying attention to copyrights in the information and content.
3.2 Integrating and re-elaborating digital content
This competence area includes modifying, improving, developing, revising and combining existing resources to create new, original and relevant content and information. In this context, individuals create new original digital content by making fundamental changes in the content produced by others, by editing, improving, changing the content produced by themselves or by others, or by mixing and comparing existing content. At the end of this process, the information obtained using different source databases and platforms contributes to the field of study and to the society in the dimension of knowledge, provided that the relevant content references are also given.
Suggestion
We encourage our colleagues to participate in other courses,which are related to the topic, on our eTwinning Professional Development Course platform.
3.3. Copyrights and Licenses
This competency includes knowing how copyrights and licenses apply to data, information and digital content, being aware of and using the relevant proprietary rights. In this context, individuals create digital content by applying licenses to the content they create, knowing which copyright the content they use falls under, knowing the differences between copyright, licensing and creative commons standards, knowing how these license types are valid. In this process, individuals pay attention to copyrights and licenses in the content creation process, while at the same time applying these intellectual property rights in the content they produce. For more on copyrights and licensing, you can visit the following sites
3.4. Programming
This area of competence is to plan and develop a clear set of instructions for a computer system to solve a specific problem or perform a specific task, to select the programs, applications, software, tools and devices needed, to make changes in the program settings, to adapt the programs and codes according to their own needs. It includes making modifications, knowing the principles of programming, having an understanding of what happens in the background during the execution of a program. In this context, individuals create digital content by changing some simple or advanced functions of software and applications (by making basic or advanced settings), making changes in the source codes of the programs, knowing different programming/coding languages and coding the programs . In this process, individuals know how the programs work in the background, what the tasks of the code structures are, the structure of the technological ecosystem, and what the programmable devices are. At the advanced level of this competency, the individual can develop applications that can be used in daily life, create simulations and create complex models.
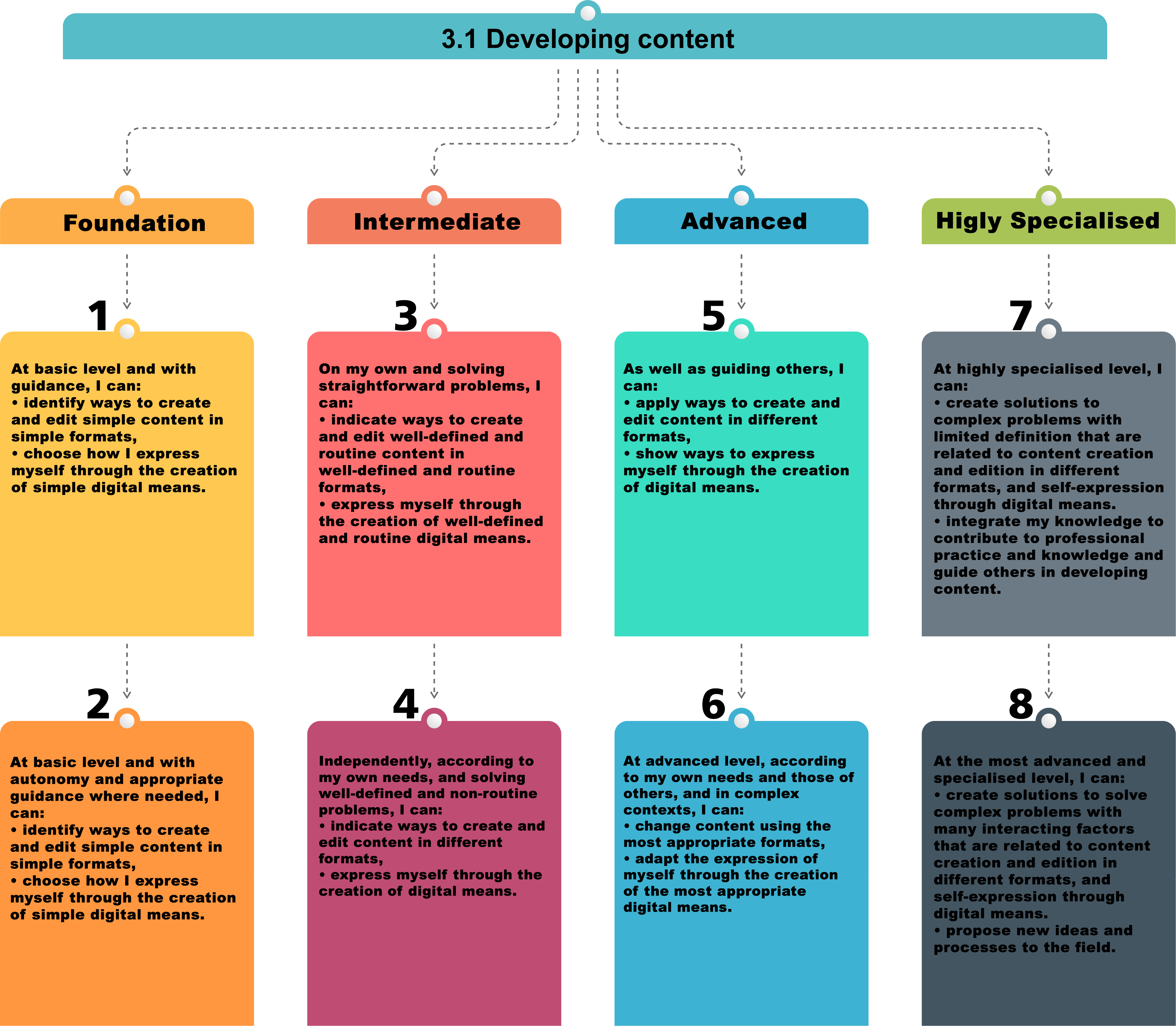
You can examine how a sub-digital competency is leveled at the Digital Content Creation competency level from the visual.
eTwinning Context with DigComp Digital Content Creation
Please watch the video of Antonella Settimi on the “Digital Content Creation” aspect of eTwinning projects.
ITT “Allievi-Sangallo” di Terni
Terni/Italy
Discussion
Module Task
- Prepare an infographic or poster or animation video promoting the eTwinning project(s) you are running in the 2021-2022 academic year. Share this digital content you have prepared by tagging your project partners in our Facebook group

Do not forget to reflect your positive feedback for at least 2 shared projects.
It is optional task. We recommend you to watch the video titled “How technology shapes the future of education” shared below.
3. Please do not forget to answer the quiz questions about the Module.